Lyme disease
Lyme disease is infectious, although not contagious, and is caused by a bacteria (Borrelia burgdorferi) being transmitted to humans by ticks. The transmission takes place through the bite of an infected tick.
If it is left untreated, this infection can eventually affect, either directly or indirectly, most body organs in an acute and / or chronic manner and lead to different effects, depending on the particular organ and the patient, and can finally result in physical and mental handicap.
The manifestation of symptoms associated with Lyme disease and tick infections may be delayed.
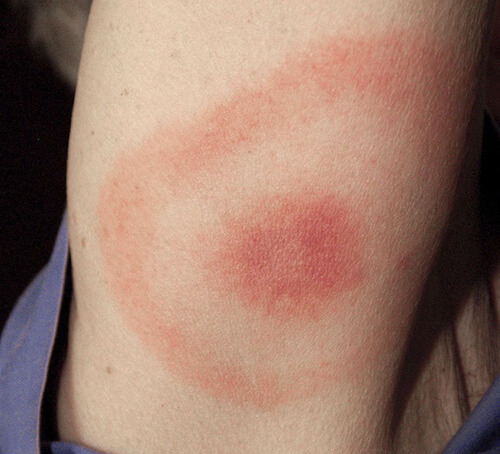
Early stage
Erythema is only present in 50% of cases. It can take different forms (circular redness or blotches) and gradually expand. It may appear up to several weeks after the bite.
The erythema may disappear by itself, but this is not a sign of healing.
The symptoms may be flu-like :
- general discomfort
- tiredness
- headhache
- shivering
- fever
- muscular and/or joint pain
- facial paralysis…
If the initial symptoms are not treated with antibiotics, there is a risk ofdissemination stage.
Dissemination stage
The signs are :
- weakness, tiredness
- intense pain and joint stiffness
- headhache
- weakness in muscles
- digestive disorders
- problems of vision
- skin rashes
- irregular heartbeat
- weight gain or weight loss
Late dissemination stage
In the long term, patients could show symptoms of :
- arthritis
- neurological disorders
- paraesthesia (abnormal sensations, tingling, burning)
- trembling
- extreme tiredness...
